SafeEyes is a Linux application which tries to protect your eyes from eye strain by reminding you to take breaks, while also providing some simple exercises.
The application was updated to version 1.1.5 (then quickly to 1.1.6 to fix a bug) recently, bringing some new features, like an option to disable SafeEyes - you can now choose to disable it for 30 minutes, 1, 2 or 3 hours, or until system restart.
Another change in the latest SafeEyes is the ability to override some of its settings. SafeEyes provides some options in its Settings window, however, even more settings can be changed by editing the safeeyes.json file (located under ~/.config/safeeyes/), such as:
- override full-screen mode and skip / take breaks based on the active window (by default, SafeEyes doesn't show the break screen when an application is used in fullscreen mode, but this can be changed; for instance, you can set SafeEyes to take a break regardless of a certain window being fullscreen);
- override individual break time;
- override individual audible alert.
These overrides are explained in detail on the SafeEyes GitHub page.
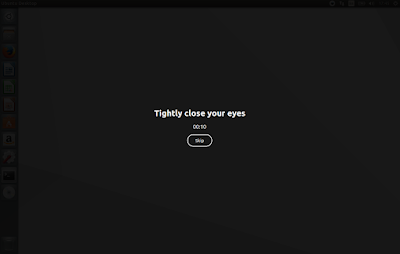 |
| The SafeEyes break screen |
Also, since our initial article about SafeEyes, the application has received quite a few improvements, including:
- optional audible alert at the end of breaks;
- Safe Eyes is now paused if the system is idle for a certain number of minutes (this is configurable from the Safe Eyes settings);
- multi-screen support;
- support for handling system suspend (stop and restart during system suspend);
- next break information in tray menu;
- multi-language support.
Install SafeEyes in Ubuntu or Linux Mint
You can install SafeEyes in Ubuntu or Linux Mint by using its official PPA. To add the PPA and install SafeEyes, use the following commands:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:slgobinath/safeeyes
sudo apt update
sudo apt install safeeyesTo download the latest SafeEyes deb, source code, report bugs, etc., see its GitHub page.


